P&L for short, also known as Income Statement in English. The income statement reflects the company's income and expenditure over a period of time (usually one quarter, half a year and one year), and reflects the company's profitability. With the balance sheet and cash flow statement, the company's three major financial statements.
简称 P&L , 英 文 亦 作Income Statement损益表反映一段时间内(通常是一季、半年及一年)公司的收入与 支出状况,反映公司的盈利能力。与 资产负债表及现金流量表合称公司 三大财务报表。
当前国际上常用的利润表格式有单步式和多步式两种。单步式是将当期收入总 额相加,然后将所有费用总额相加,一次 计算出当期收益的方式,其特点是所提 供的信息都是原始数据,便于理解;多步 式是将各种利润分多步计算求得净利润 的方式,便于使用人对企业经营情况和 盈利能力进行比较和分析。
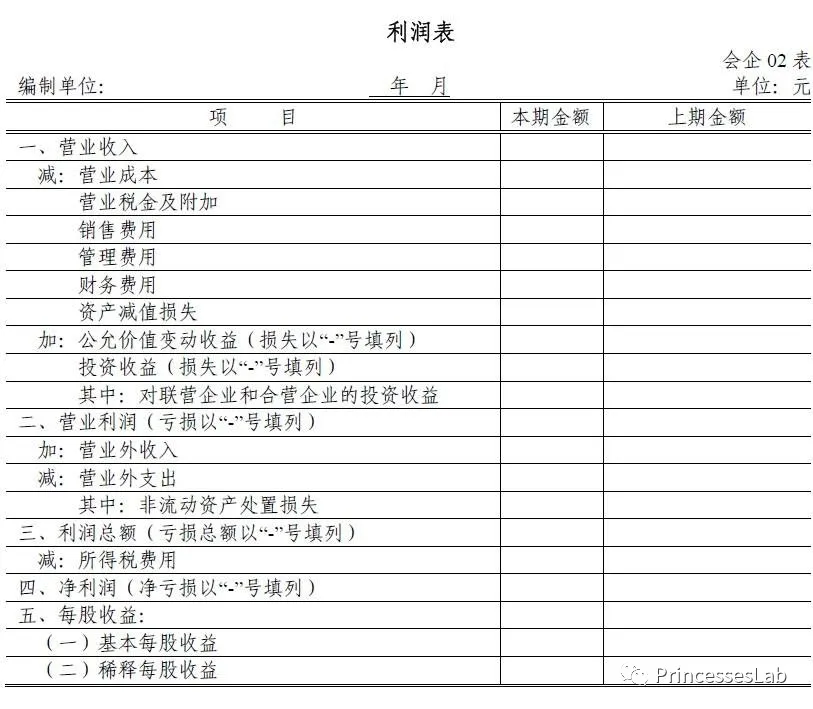
Cash Flow Statement(现金流量表)
Important financial statements other than the company's balance sheet and income statement show the company's cash inflows and outflows over a period of time and explain where the changes in cash assets come from during the period. Cash flow statements generally classify cash flows into three categories: 1. Operating cash flows from operating activities, which reflect net cash inflows or outflows from sales of products and services, equal to profits plus non-cash expenses such as depreciation and amortization, and then include changes in current assets other than cash and current liabilities other than short-term loans. Reduction of current assets represents cash inflows, while reduction of current liabilities represents cash outflows; 2. Cash flow from financing activities, which reflects the cash flow of a company in financing activities such as issuing stocks or bonds, lending to banks, repaying debts or distributing dividends; 3. Cash flow from investing activities, which reflects the company's investment or sale of fixed assets. Cash flow generated.
公司资产负债表及损益表以外的重 要财务报表,显示公司在一段时间内 现金进出的情况,解释期间现金资产 的变动从何而来。现金流量表一般会 将现金流量归为三大类:1.经营现金 流 (cash flow from operating activities),反映产品及服务销售所产 生的现金流入或流出净额,等于盈利 加上非现金费用如折旧及摊销,再计 入现金以外的流动资产及短期贷款 以外的流动负债的变动。流动资产减 少代表现金流入,流动负债减少则代 表现金流出;2.融资现金流(cash flow from financing activities),反映公司在 发行股票或债券,向银行贷款,还债 或派发股息等融资活动上的现金流;3.投 资 现 金 流 (cash flow from investing activities),反映公司投资或 出售固定资产所产生的现金流。
对于现金流量表需要注意,在编制该表 时采用的会计准则是收付实现制。现金 流量表的出现,主要是要反映出资产负 债表中各个项目对现金流量的影响,并 根据其用途划分为经营、投资及融资三 个活动分类。现金流量表可用于分析一 家机构在短期内有没有足够现金去应付开销。
Debt equity ratio(负债权益比率)
Debt equity ratio is used to assess the relevant risks and leverage of the relevant securities holders. The total amount of liabilities and interests reflects the strength of the financial structure of the unit under review and the degree to which the creditor's capital is protected by the owner's rights and interests. The high ratio of liabilities to equity indicates that the total capital of the audited unit is high in liabilities, so the degree of protection of liabilities to capital is weak; the low ratio of liabilities to equity indicates that the audited unit has strong financial strength, and therefore the degree of protection of liabilities to capital is high. In the broad sense of capital structure, debt-equity ratio refers to the ratio between the total debt of an enterprise and the owner's equity (shareholder's equity), also known as the property right ratio. In the narrow sense of capital structure, the debt-equity ratio refers to the ratio between the long-term debt of an enterprise and the owner's equity (shareholder's equity).
负债权益比率是指用于评估有关证券持有人的相关风险和杠杆率。反映被审单位财务结构的强弱,以及债权人的资本受到所有者权益的保障程度。负债权益比率高,说明被审单位总资本中负债资本高,因而对负债资本的保障程度较弱;负债权益比率低,则说明被审单位本身的财务实力较强,因而对负债资本的保障程度较高。在广义的资本结构含义下,负债权益比率是指企业负债总额与所有者权益(股东权益)之间的比值,又称为产权比率。在狭义的资本结构含义下,负债权益比率是指企业 的长期负债与所有者权益(股东权益) 之间的比值。
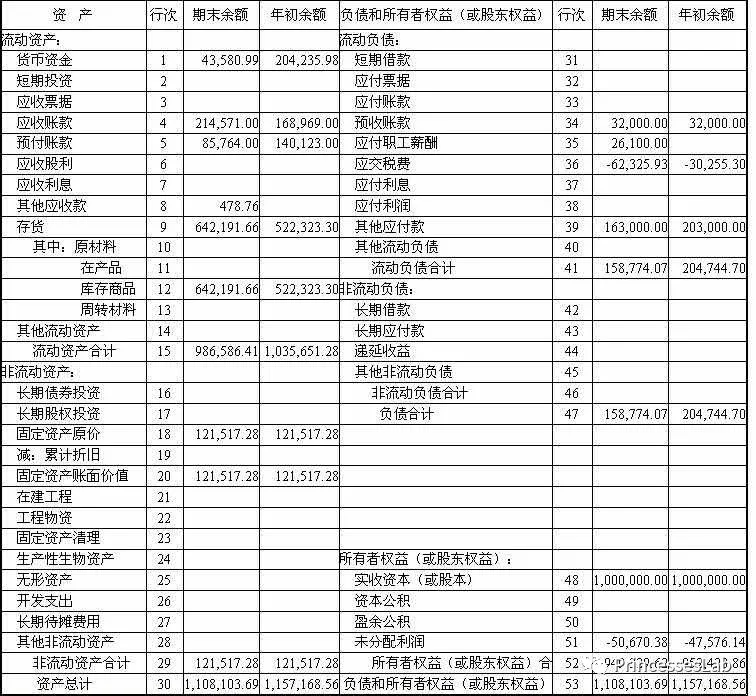
Dividend Cover(股息保障倍数)
The extent to which a company's dividend and/or interest payments are matched or exceeded by its earnings. Expressed as a multiple. The company's rating in the market increases as the multiple rises.
公司向股东支付股息能力的指标,由可派发股息的盈余( 即股东应占溢利)除以股息得出。对于有稳定派息记录的公司来说,倍数越高,市场对其评价越高。
Profit Margin/Rate(利润率)
Profit rate is the financial ratio that reflects the profitability of a company. It is expressed as a percentage by dividing profits over a period of time by operating income. Roughly speaking, if the profit margin is 20%, it means that every 100 yuan business can earn 20 yuan. Commonly used profit margins include gross profit, net profit margin and operating profit margin. The denominator of these three ratios is operating income. The numerator is gross profit (income minus direct cost of goods), net profit (income minus all expenses and expenses) and operating profit (gross profit minus operating expenses).
利润率是反映公司盈利能力的财务 比率,由一段时间内的利润除以营业收入得出,以百分比表达。粗略而言,若利润率为 20%,代表每做 100元的生意可赚20元。
常用的利润率包括 毛利率、净利润率以及营业利润率,此三比率的分母均为营业收入,分子则分别是毛利(收入减掉货物的直接成本)、净利(收入减去所有的费用与支出)和营运利润(毛利减去营业费用)。
Current Ratio(流动比率)
Liquidity ratio is a measure of a company's ability to pay short-term debt. It is derived by dividing current assets by current liabilities. Current assets include cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable and inventory, while current liabilities are equal to the sum of short-term loans and accounts payable. The normal range of liquidity ratio is 0.5-2.0, but we must be careful to interpret this liquidity ratio. A higher ratio may mean that the company has too much idle cash, customers are in arrears with large amounts of accounts, or the company needs a lot of inventory for its operations. Lower ratios do not necessarily mean that companies are at risk of not being able to repay short-term debt. They may simply be based on cash payments in their industries (such as restaurants that usually have little or no accounts receivable), or their operations do not require too much inventory (such as most service companies), or customers in their industries pay more slowly (such as construction).
流动比率是衡量公司偿付短期债务 能力的一项指标,由流动资产除以流动负债得出(流动比率=流动资产/流动负债)。流动资产包括现金及现金等价物、应收账款和库存,而流动负债则等于短期贷款和应付账款之 和。流动比率的正常范围值为 0.5~ 2.0,但解读这个流动性比率必须谨慎。较高的比率可能意 味着公司有太多闲置现金、客户拖欠 大笔账款,或者公司的经营需要大量 的库存。较低的比率并不一定意味着 公司有无法偿还短期债务的风险,可 能只是因为公司所在行业以支付现 金为标准(例如餐馆通常只有很少或 没有应收账款),或其经营不需要太 多的库存(例如大多数服务业公司), 或所在行业客户支付的速度较慢(例如建筑业)。
EPS(每股净盈利)
EPS is the abbreviation of Earnings Per Share, which refers to the after-tax profit per share of common stock, also known as "earnings per share". EPS is the final result of the company's profitability. The high earnings per share represents the high profitability of the company per unit of capital, which means that the company has some better ability -- product marketing, technical ability, management ability, etc., so that the company can use less resources to create higher profits.
EPS 是每股盈余(英文全称 Earnings Per Share)的缩写,指普通股每股税后利润,也称为“每股收益”。EPS 为公司获利能力的最后结果。每股盈余 高代表着公司每单位资本额的获利 能力高,这表示公司具有某种较佳的 能力——产品行销、技术能力、管理能力等等,使得公司可以用较少的资源创造出较高的获利。
每股利润过高的话,该公司的市盈率就(Price Earnings Ratio)会较低,反映在财务报表以及上市公司在证券交易所的年度财务报告中,会给股民该公司股价存在低估印象,对公司股价上扬有正面影响。
BVPS(每股面值)
Book value equals total assets minus total liabilities. Book value per share (BVPS) equals book value divided by the number of shares outstanding. It is the same as shareholders' equity. BVPS is used in the calculation of the price/book ratio (share price divided by BVPS). Price/book is the ultimate measure of how much investors think a company's assets are worth and it equals the share price divided by the BVPS. A price/book ratio should be higher than one; otherwise the market is pricing the assets below their replacement value. Companies with price/book ratios well below one automatically become takeover targets as sector rivals will consider launching a bid for their stock rather than investing in new plant and equipment. Price/book is especially relevant for capital-intensive manufacturing firms. Service industry companies with few fixed assets typically trade at high price/book ratios.
英文 Book value Per Share 的缩写。账面净值(book value)等同于股东权益 (shareholders' euqity),即总资产减去总负债。每股账面净值等于账面净值除以已发行股数。 股价除以每股账面净值即得出股价净值比(price/book ratio),这是投资者衡量公司资产价值的关键指标。股价净值比若低于 1,则代表市场对公司 资 产 的 定 价 低 于 其 重 置 成 本 (replacement cost)。若股价净值比远 低于 1,公司通常会成为收购目标, 因为觊觎此公司资产的同业竞争者 会考虑收购这家公司的股权以取得 资产,而不是自己进行厂房和设备的 投资。股价净值比对资本密集型的制 造业公司特别有意义。 服务业因固定资产较少,股价净值比通常比较高。
股票市价高于账面价值越多,越是表明投资者认为这个企业有希望、有潜力,否则,说明市场不看好该企业。
Minority Interest(少数股东权益)
An important but non-controlling outside ownership stake in a company or subsidiary. Also used to describe the share of a parent company's net profits or net assets that are attributable to those minority shareholders in partially-owned subsidiaries.
在一家公司中,不为控股股东所持有 的股权称为少数股东权益,通常合共不会超过股权的 50%。 在集团财务报表上,资产负债表上的少数股东权益代表在集团的子公司中持少数股权的股东应占的净资产,损益表上的少数股东权益代表子公司中的少数股东应占的净利。
Working Capital(营运资本)
Working Capital usually refers to net working capital and is the resource that a company can use to finance day-to-day operations. It is calculated by taking current liabilities from current assets.营运资金等于流动资产减去流动负 债,是衡量公司能动用多少流动资产 来改善营运或扩充业务的一个指标。
Earnings Before Interest and Tax(息税前利润)
The profit without deducting interest and income tax, that is, the profit before paying income tax without considering interest. It can also be called pre-interest and pre-tax profit. Interest and pre-tax profit, as its name implies, refers to the profit before interest and income tax are paid.
无论企业营业利润多少,债务利息和优 先股的股利都是固定不变的。当息税前利润增大时,每一元盈余所负担的固定 财务费用就会相对减少,这能给普通股 股东带来更多的盈余。
ROE Return on Equity (每股收益)
The rate of return on net assets, also known as the rate of return on equity/net value/rate of return on equity/rate of return on equity/profit on equity/profit on equity/profit on equity/profit on net assets, is the percentage of net profit and average shareholder's equity. It is the percentage rate of company's after-tax profit divided by net assets. This index reflects the level of return on equity of shareholders and is used to measure the company's use of its own assets. Capital efficiency. The higher the index value, the higher the return of investment. This index reflects the ability of self-owned capital to obtain net income.
净资产收益率 ROE,净资产收益率又称股东权益报酬率/净值报酬率/权益报酬率/权益利润率/净资产利润率,是净利润与平均股东权益的百分比,是公司税后利润除以净资产得到的 百分比率,该指标反映股东权益的收益水平,用以衡量公司运用自有资本的效率。指标值越高,说明投资带来的收益越高。该指标体现了自有资本获得净收益的能力。
Weighted Average Cost of Capital(加权平均资本成本)
Weighted Average Cost of Capital. WACC is used to measure whether a potential investment will generate an adequate return. It is the cost of debt and equity, weighted by their relative contribution to overall costs both in the proportion of the funding and the cost of the related interest or dividend payments.
WACC 代表公司整体平均资金成本,可用来衡量一个项目是否值 得投资;项目的回报必 须不低于WACC。 计算 WACC 时,先算出构 成公司资本结构的各个项目如普通 股、优先股、公司债及其他长期负债各自的资金成本或要求回报率,然后 将这些回报率按各项目在资本结构中的权重加权,即可算出。
计算方法为每种资本的成本乘以占总资本的比重,然后将各种资本得出的数目加起来
WACC=(E/V)×Re+(D/V)×Rd×(1-Tc)
其中:WACC=Weighted Average Cost of Capital(加权平均资本成本)
Re = 股本成本
Rd = 债务成本
E = 公司股本的市场价值
D = 公司债务的市场价值
V = E + D
E/V = 股本占融资总额的百分比 D/V = 债务占融资总额的百分比 Tc = 企业税率